Asim Rashid
PhD, Jönköping University
Gallery
Here are some of simulation results from my amateur work.
Tube Hydroforming
As the tube will undergo large deformations and there are other nonlinearities involved, the implicit solver is set to consider these nonlinearities (by turning on Nlgeom option in Abaqus).
Bending of staple
This problem is highly nonlinear as it involves contact with large sliding movement and material plasticity. The implicit solver suffers from convergence difficulties. The explicit solver is used to solve this problem as it does not perfrom Newton-Raphson iterations to converge the solution. To make sure that an acceptable quasi-static solution is obtained, step time is choosen such that kinetic energy of the model is considerably smaller than the intrnal energy.
Contact pressure over piston ring
The initial geometry of the piston ring consists of circular arc. As the initial size of the ring is larger than cylinder bore, so contact algorithm should solve interference and fit the ring inside the cyclinder. By taking advantage of symmetry, only half of assembly is simulated.
Projectile Penetration into Steel Plate
This simulation illustrates the impact of a rigid projectile onto a plate. The material definition includes a failure model which allows the projectile to perforate the plate. During the analysis, failed elements are removed from the model.
Bumper Crash Simulation
This simulation illustrates vehicle crash while only bumper is modeled. The mass of the vehicle is attached to a reference point representing the center of mass. The objective of the analysis is to predict the history of deformation.Frame Crash Simulation
This simulation illustrates vehicle frame crash while mass of the engine is attached to appropriate points. The objective of the analysis is to predict the history of deformation.Door Seal
In this study, behavior of a door seal due to closing of door is simulated. The seal is modeled with Hyperelastic Mooney-Rivlin material model. The implicit solver suffers from convergence difficulties therefore explicit solver is used instead.Boot Seal
The simulation illustrates the deformation of a boot seal due to angular movement of the shaft. The contact problem involves the solution of interference between seal and shaft and later self-contact of the seal. The seal is modeled with Hyperelastic Polynomial material model.O-Ring as a Radial Seal
This simulation illustrates the behaviour of a radial seal while the parts move relative to each other. At the end, an air pressure is also applied to study the behavior of seal in pressurised environment.
Slider Mechanism
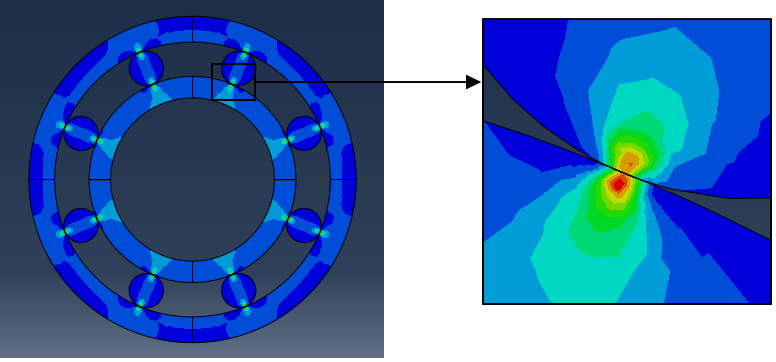
The slider mechanism consists of a cylinder and reciprocating piston. The piston is placed tightly (initial overclosure) inside the cylinder. A harmonic sliding motion is applied to the piston. Contact interaction between piston and cylinder uses classical Coulomb friction model in which friction coefficient is slip-rate dependent. At the end of simulation, time history of frictional shear forces is shown. It can be seen that as the piston starts moving it changes from 'stick' to 'slip'. When the piston reaches other end, it goes from 'slip' to 'stick'. It reverses its direction and again slips.Stress Distribution in Roller Bearing
Highest stresses appear below the load carrying surface. Cyclic repetition of these stresses results in cracks which extend to the surface after some duration. This could result in material fragments break away, known as flaking.